On this Page
STRUCTURE
AND FUNCTION
KIDNEYS
- A FILTERING MACHINE
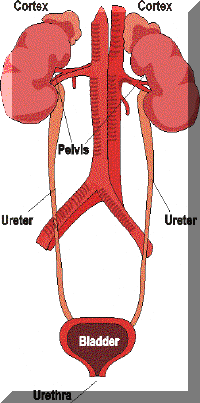
Two kidneys (right and left, situated at lumber
region of abdomen) plays significant role to remove waste products from the
blood and excrete what we call urine.
Nephrons (one million in each kidney) are
the basic functional unit where plasma (part) of the blood passes through Glomeruler
tuft (upper part of nephron) gets filtered (120 cc per minute) followed
by selective reabsorption of the salts and water in tube like structure (loop of
Henele) which opens into collecting duct, and by the act of micturation urine
passes through Urethra.
Normally 1000 cc to 1500 cc of urine
excreted daily and different parts of Nephrons play important roles in urine
formation, therefore , it is imperative to have a look on the structure and
function of each portion of Nephron and on the reasons that different diseases
hamper different parts of the Nephron leading to renal failure.
Kidney
image (Click to Enlarge)
Worsening of renal function causes
retention of waste products in the blood (Urea, Uric acid, Creatinin and
Ammonia) alongwith inorganic substances (Sodium, Potassium Chloride, Calcium,
Phosphates and Sulphates) and accumulation of water in the body (not required).
Worsening is termed as acute when occurs in few days or chronic when it takes
months to years to damage health of a person.
The degree of renal failure is
assessed on Blood Urea level, Serum Creatinin level, BUN, Creatinin ratio or
estimating. Glameruler filtration rate, Radionuclide studies, Ultrasonography,
I.V.P (Intravenous Pyelogram) Computed Tomograpgy (CT) Scanning, Magnetic
Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Renal Biopsy.
MAJOR
CAUSES OF RENAL FAILURE
Glomerulopathies
Primary
glomerular diseases:
Secondary glomerular diseases:
Tubulointerstitial
Nephritis
Hereditary Diseases
Obstructive Nephropathies
Vascular Diseases
MANIFESTATIONS
OF RENAL FAILURE
-
Blood Potassium level gets
increased.
-
Disorder of Acid-base balance.
-
Sulphates and Phosphates
increased and H+ ion get decreased.
-
Hypertension - Because of Salt
and Water retention.
-
Pericarditis - When BUN
concentration exceeds 100 mg/dL.
-
Congestive Heart Failure.
-
Anemia - Because of decrease of
Erthroprotein.
-
Coagulopathy - The coagulopathy
of chronic renal failure is mainly caused by Platelet dysfunction.
-
Neurological Complications -
High urea level causes encephlopathy.
-
Mineral Metabolism - Disorder of
Calcium and Phosphorus causes Osteodystrophy.
-
Endocrine Disorders - Due to
peripheral insuline resistance.
TREATMENT
Apart from Dietary Management
Protein, Salt, Water, Potassium, Phosphorus, Magnesium restriction.
Haemodialysis
Blood is taken out of the body,
passes through a machine with special filter - system to remove waste products,
re-enter into body.
Peritoneal Dialysis
Where Dialysate (a solution)
enters the peritoneal cavity through a catheter, exchanges takes place and
Dialysate is taken out through a catheter after few hours and fresh Dialysate
solution is injected into the peritoneal cavity.
Kidney Transplantation
Alternative Medicine
HERBAL
WAY OF TREATMENT
For More Information Contact:
Markaz-Al-Shifa
Tel: 92-42-7322416
FAX: 92-42-7119950
Email: farz60@wol.net.pk
|